vLLM MCP Server
Exposes vLLM capabilities to AI assistants, enabling chat completions, model management, and platform-aware container control with automatic detection of Docker/Podman and GPU availability across Linux, macOS, and Windows.
README
vLLM MCP Server
A Model Context Protocol (MCP) server that exposes vLLM capabilities to AI assistants like Claude, Cursor, and other MCP-compatible clients.
Features
- 🚀 Chat & Completion: Send chat messages and text completions to vLLM
- 📋 Model Management: List and inspect available models
- 📊 Server Monitoring: Check server health and performance metrics
- 🐳 Platform-Aware Container Control: Supports both Podman and Docker. Automatically detects your platform (Linux/macOS/Windows) and GPU availability, selecting the appropriate container image and optimal settings (e.g.,
max_model_len) - 📈 Benchmarking: Run GuideLLM benchmarks (optional)
- 💬 Pre-defined Prompts: Use curated system prompts for common tasks
Demo
Start vLLM Server
Use the start_vllm tool to launch a vLLM container with automatic platform detection:
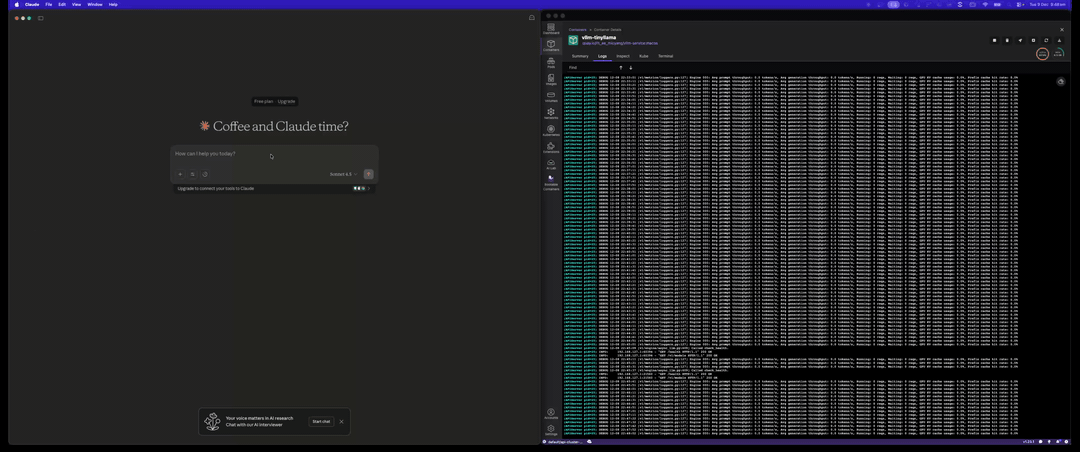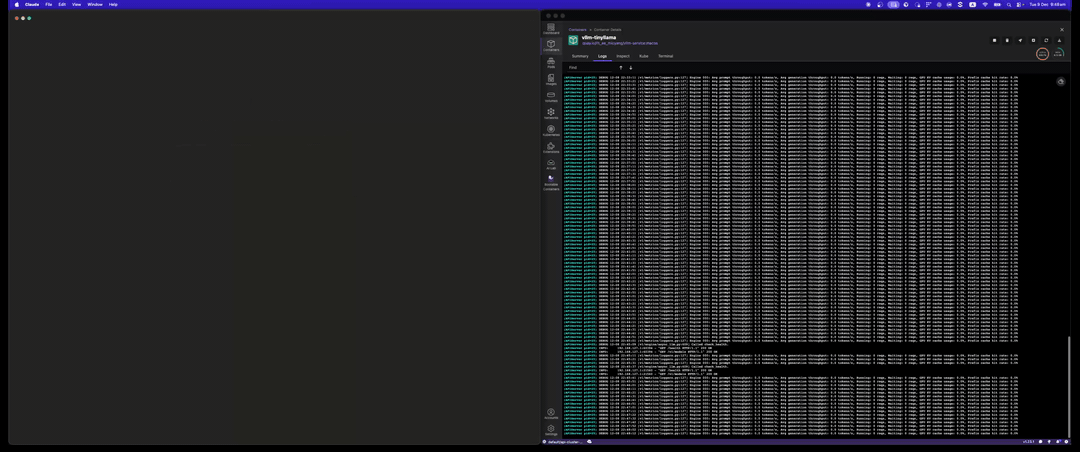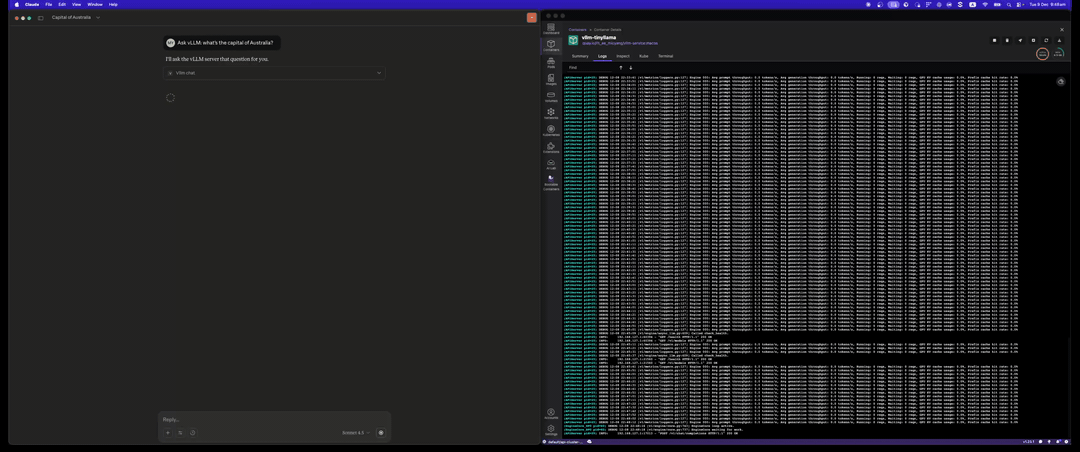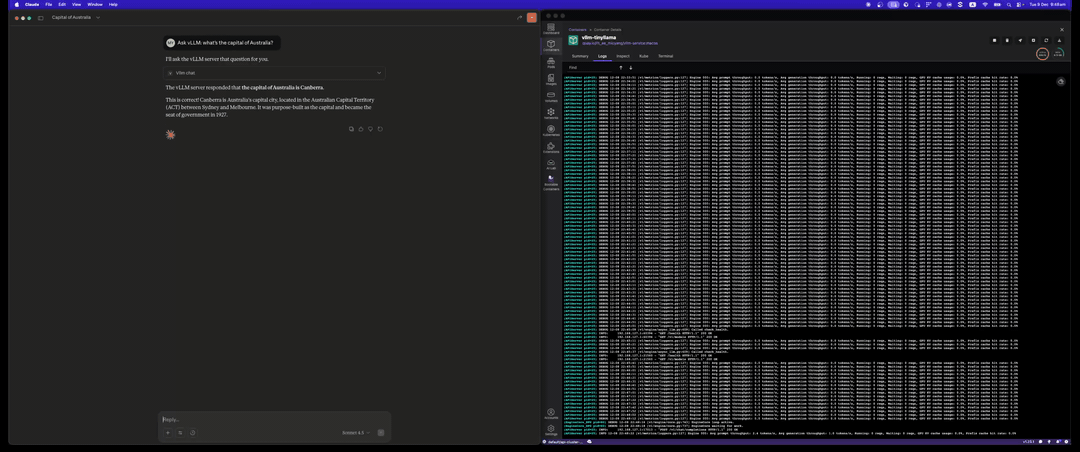
Chat with vLLM
Send chat messages using the vllm_chat tool:
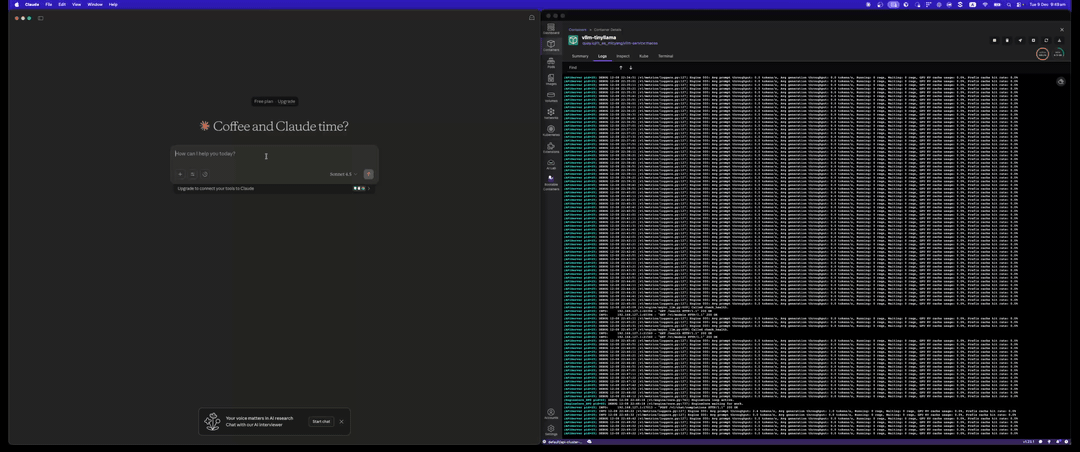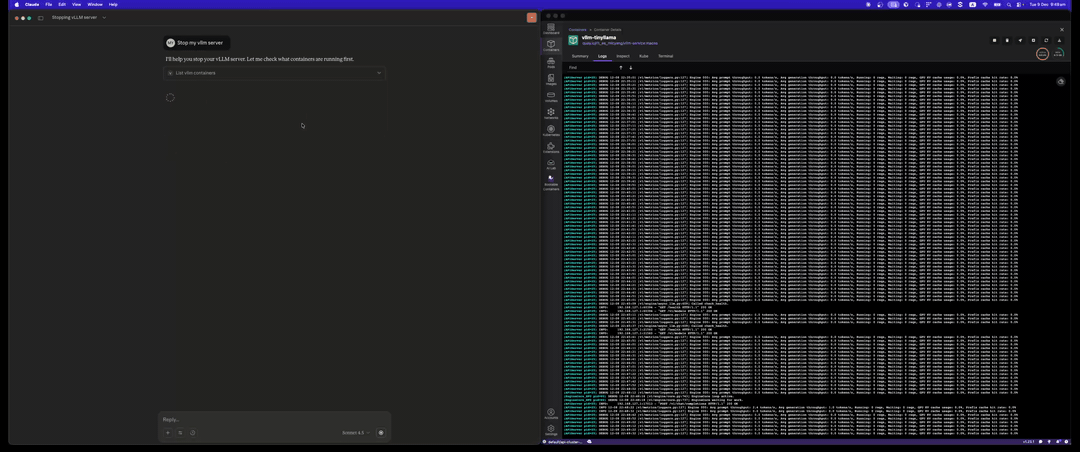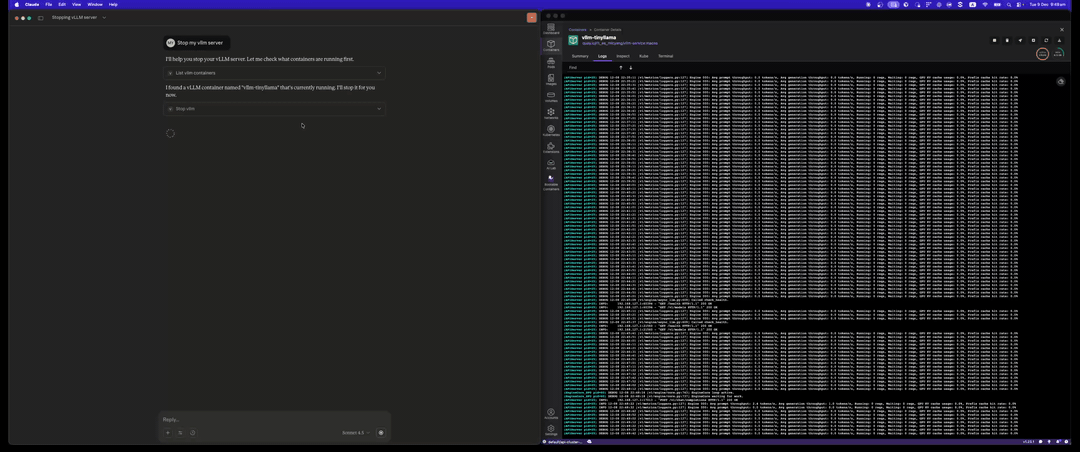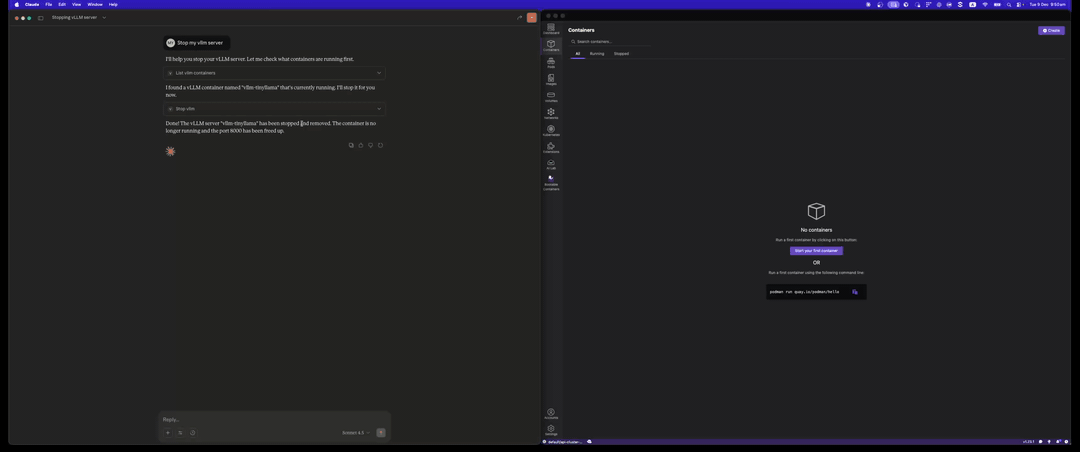
Stop vLLM Server
Clean up with the stop_vllm tool:
Installation
Using uvx (Recommended)
uvx vllm-mcp-server
Using pip
pip install vllm-mcp-server
From Source
git clone https://github.com/micytao/vllm-mcp-server.git
cd vllm-mcp-server
pip install -e .
Quick Start
1. Start a vLLM Server
You can either start a vLLM server manually or let the MCP server manage it via Docker.
Option A: Let MCP Server Manage Docker (Recommended)
The MCP server can automatically start/stop vLLM containers with platform detection. Just configure your MCP client (step 2) and use the start_vllm tool.
Option B: Manual Container Setup (Podman or Docker)
Replace podman with docker if using Docker.
Linux/Windows with NVIDIA GPU:
podman run --device nvidia.com/gpu=all -p 8000:8000 \
vllm/vllm-openai:latest \
--model TinyLlama/TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0
macOS (Apple Silicon / Intel):
podman run -p 8000:8000 \
quay.io/rh_ee_micyang/vllm-mac:v0.11.0 \
--model TinyLlama/TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0 \
--device cpu --dtype bfloat16
Linux/Windows CPU-only:
podman run -p 8000:8000 \
quay.io/rh_ee_micyang/vllm-cpu:v0.11.0 \
--model TinyLlama/TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0 \
--device cpu --dtype bfloat16
Option C: Native vLLM Installation
vllm serve TinyLlama/TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0
2. Configure Your MCP Client
Cursor
Add to ~/.cursor/mcp.json:
{
"mcpServers": {
"vllm": {
"command": "uvx",
"args": ["vllm-mcp-server"],
"env": {
"VLLM_BASE_URL": "http://localhost:8000",
"VLLM_MODEL": "TinyLlama/TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0",
"VLLM_HF_TOKEN": "hf_your_token_here"
}
}
}
}
Note:
VLLM_HF_TOKENis required for gated models like Llama. Get your token from HuggingFace Settings.
Claude Desktop
Add to your Claude Desktop configuration:
{
"mcpServers": {
"vllm": {
"command": "uvx",
"args": ["vllm-mcp-server"],
"env": {
"VLLM_BASE_URL": "http://localhost:8000",
"VLLM_HF_TOKEN": "hf_your_token_here"
}
}
}
}
3. Use the Tools
Once configured, you can use these tools in your AI assistant:
Server Management:
start_vllm- Start a vLLM container (auto-detects platform & GPU)stop_vllm- Stop a running containerget_platform_status- Check platform, Docker, and GPU statusvllm_status- Check vLLM server health
Inference:
vllm_chat- Send chat messagesvllm_complete- Generate text completions
Model Management:
list_models- List available modelsget_model_info- Get model details
Configuration
Configure the server using environment variables:
| Variable | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|
VLLM_BASE_URL |
vLLM server URL | http://localhost:8000 |
VLLM_API_KEY |
API key (if required) | None |
VLLM_MODEL |
Default model to use | None (auto-detect) |
VLLM_HF_TOKEN |
HuggingFace token for gated models (e.g., Llama) | None |
VLLM_DEFAULT_TEMPERATURE |
Default temperature | 0.7 |
VLLM_DEFAULT_MAX_TOKENS |
Default max tokens | 1024 |
VLLM_DEFAULT_TIMEOUT |
Request timeout (seconds) | 60.0 |
VLLM_CONTAINER_RUNTIME |
Container runtime (podman, docker, or auto) |
None (auto-detect, prefers Podman) |
VLLM_DOCKER_IMAGE |
Container image (GPU mode) | vllm/vllm-openai:latest |
VLLM_DOCKER_IMAGE_MACOS |
Container image (macOS) | quay.io/rh_ee_micyang/vllm-mac:v0.11.0 |
VLLM_DOCKER_IMAGE_CPU |
Container image (CPU mode) | quay.io/rh_ee_micyang/vllm-cpu:v0.11.0 |
VLLM_CONTAINER_NAME |
Container name | vllm-server |
VLLM_GPU_MEMORY_UTILIZATION |
GPU memory fraction | 0.9 |
Available Tools
P0 (Core)
vllm_chat
Send chat messages to vLLM with multi-turn conversation support.
{
"messages": [
{"role": "system", "content": "You are a helpful assistant."},
{"role": "user", "content": "Hello!"}
],
"temperature": 0.7,
"max_tokens": 1024
}
vllm_complete
Generate text completions.
{
"prompt": "def fibonacci(n):",
"max_tokens": 200,
"stop": ["\n\n"]
}
P1 (Model Management)
list_models
List all available models on the vLLM server.
get_model_info
Get detailed information about a specific model.
{
"model_id": "TinyLlama/TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0"
}
P2 (Status)
vllm_status
Check the health and status of the vLLM server.
P3 (Server Control - Platform Aware)
The server control tools support both Podman (preferred) and Docker, automatically detecting your platform and GPU availability:
| Platform | GPU Support | Container Image | Default max_model_len |
|---|---|---|---|
| Linux (GPU) | ✅ NVIDIA | vllm/vllm-openai:latest |
8096 |
| Linux (CPU) | ❌ | quay.io/rh_ee_micyang/vllm-cpu:v0.11.0 |
2048 |
| macOS (Apple Silicon) | ❌ | quay.io/rh_ee_micyang/vllm-mac:v0.11.0 |
2048 |
| macOS (Intel) | ❌ | quay.io/rh_ee_micyang/vllm-mac:v0.11.0 |
2048 |
| Windows (GPU) | ✅ NVIDIA | vllm/vllm-openai:latest |
8096 |
| Windows (CPU) | ❌ | quay.io/rh_ee_micyang/vllm-cpu:v0.11.0 |
2048 |
Note: The
max_model_lenis automatically set based on the detected mode (CPU vs GPU). CPU mode uses 2048 to match vLLM'smax_num_batched_tokenslimit, while GPU mode uses 8096 for larger context. You can override this by explicitly passingmax_model_lentostart_vllm.
start_vllm
Start a vLLM server in a Docker container with automatic platform detection.
{
"model": "TinyLlama/TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0",
"port": 8000,
"gpu_memory_utilization": 0.9,
"cpu_only": false,
"tensor_parallel_size": 1,
"max_model_len": null,
"dtype": "auto"
}
Note: If
max_model_lenis not specified (ornull), it defaults to 2048 for CPU mode or 8096 for GPU mode.
stop_vllm
Stop a running vLLM Docker container.
{
"container_name": "vllm-server",
"remove": true,
"timeout": 10
}
restart_vllm
Restart a vLLM container.
list_vllm_containers
List all vLLM Docker containers.
{
"all": true
}
get_vllm_logs
Get container logs to monitor loading progress.
{
"container_name": "vllm-server",
"tail": 100
}
get_platform_status
Get detailed platform, Docker, and GPU status information.
run_benchmark
Run a GuideLLM benchmark against the server.
{
"rate": "sweep",
"max_seconds": 120,
"data": "emulated"
}
Resources
The server exposes these MCP resources:
vllm://status- Current server statusvllm://metrics- Performance metricsvllm://config- Current configurationvllm://platform- Platform, Docker, and GPU information
Prompts
Pre-defined prompts for common tasks:
coding_assistant- Expert coding helpcode_reviewer- Code review feedbacktechnical_writer- Documentation writingdebugger- Debugging assistancearchitect- System design helpdata_analyst- Data analysisml_engineer- ML/AI development
Development
Setup
# Clone the repository
git clone https://github.com/micytao/vllm-mcp-server.git
cd vllm-mcp-server
# Install uv if you haven't already
curl -LsSf https://astral.sh/uv/install.sh | sh
# Create virtual environment and install dependencies
uv venv
source .venv/bin/activate # or `.venv\Scripts\activate` on Windows
# Install with dev dependencies
uv pip install -e ".[dev]"
Local Development with Cursor
For debugging and local development, configure Cursor to run from source using uv run instead of uvx:
Add to ~/.cursor/mcp.json:
{
"mcpServers": {
"vllm": {
"command": "uv",
"args": [
"--directory",
"/path/to/vllm-mcp-server",
"run",
"vllm-mcp-server"
],
"env": {
"VLLM_BASE_URL": "http://localhost:8000",
"VLLM_HF_TOKEN": "hf_your_token_here",
"VLLM_CONTAINER_RUNTIME": "podman"
}
}
}
}
This runs the MCP server directly from your local source code, so any changes you make will be reflected immediately after restarting Cursor.
Running Tests
uv run pytest
Code Formatting
uv run ruff check --fix .
uv run ruff format .
Architecture
vllm-mcp-server/
├── src/vllm_mcp_server/
│ ├── server.py # Main MCP server entry point
│ ├── tools/ # MCP tool implementations
│ │ ├── chat.py # Chat/completion tools
│ │ ├── models.py # Model management tools
│ │ ├── server_control.py # Docker container control
│ │ └── benchmark.py # GuideLLM integration
│ ├── resources/ # MCP resource implementations
│ │ ├── server_status.py # Server health resource
│ │ └── metrics.py # Prometheus metrics resource
│ ├── prompts/ # Pre-defined prompts
│ │ └── system_prompts.py # Curated system prompts
│ └── utils/ # Utilities
│ ├── config.py # Configuration management
│ └── vllm_client.py # vLLM API client
├── tests/ # Test suite
├── examples/ # Configuration examples
├── pyproject.toml # Project configuration
└── README.md # This file
License
Apache License 2.0 - see LICENSE for details.
Contributing
Contributions are welcome! Please feel free to submit a Pull Request.
Acknowledgments
Recommended Servers
playwright-mcp
A Model Context Protocol server that enables LLMs to interact with web pages through structured accessibility snapshots without requiring vision models or screenshots.
Magic Component Platform (MCP)
An AI-powered tool that generates modern UI components from natural language descriptions, integrating with popular IDEs to streamline UI development workflow.
Audiense Insights MCP Server
Enables interaction with Audiense Insights accounts via the Model Context Protocol, facilitating the extraction and analysis of marketing insights and audience data including demographics, behavior, and influencer engagement.
VeyraX MCP
Single MCP tool to connect all your favorite tools: Gmail, Calendar and 40 more.
Kagi MCP Server
An MCP server that integrates Kagi search capabilities with Claude AI, enabling Claude to perform real-time web searches when answering questions that require up-to-date information.
graphlit-mcp-server
The Model Context Protocol (MCP) Server enables integration between MCP clients and the Graphlit service. Ingest anything from Slack to Gmail to podcast feeds, in addition to web crawling, into a Graphlit project - and then retrieve relevant contents from the MCP client.
Qdrant Server
This repository is an example of how to create a MCP server for Qdrant, a vector search engine.
Neon Database
MCP server for interacting with Neon Management API and databases
Exa Search
A Model Context Protocol (MCP) server lets AI assistants like Claude use the Exa AI Search API for web searches. This setup allows AI models to get real-time web information in a safe and controlled way.
E2B
Using MCP to run code via e2b.

